Git
Git is distributed version control system which is free and open source software (FOSS). It is a tool to track the changes in the code. We save an initial version of code in the git and then update over the time. We can look back all the changes done so far. Github is the website to host the repositories online.
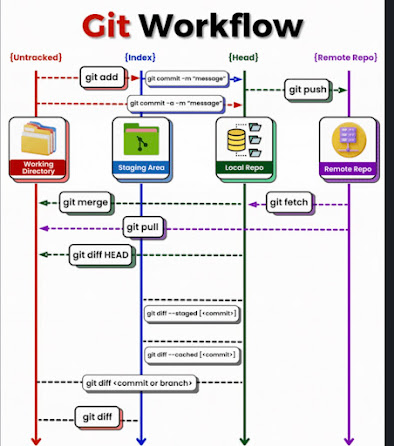
Once we have made changes local repository on the computer and ready to put in git, we need to tell git to track them through add command, save file through commit command and then upload the changes to remote repository using push command. Thus we can keep track the version history and also isolate the changes.
SSH (Secure SHell protocol is used for authentication and it is secure and convenient way to log into remote servers) keys need to be generated which consists of pair of keys, private and public keys. Public key is shared with the world via GitHub while the private key is kept secured on one's computer. When we try to connect with GitHub, SSH client provides private key to prove who you are. The GitHub then verifies with the corresponding public key.
Work Flow
Git Branching
Master Branch : The main branch (often named main or master) represents the stable and production-ready version of the code. Feature branches are created and merged into the main branch once the new features are thoroughly tested and approved.
Feature Branch: A feature branch is created to work on a specific feature or enhancement. It allows developers to isolate their work from the main codebase until the feature is complete and ready for review.
Hotfix Branch: A hotfix branch is created to address critical issues or bugs in the production code. It allows developers to make urgent fixes without disrupting ongoing development in feature branches.
Uses
It enables tracking changes in files over time, providing developers with a comprehensive history of revisions. This decentralised approach allows for collaboration among multiple developers, facilitating simultaneous work on different aspects of a project.
One of its key features is branching and merging, which supports parallel development by allowing developers to work on separate branches of code and later integrate their changes seamlessly. This promotes an efficient and organized workflow, essential for large-scale projects.
Git ensures data integrity and backup through its robust system, minimizing the risk of data loss or corruption. Its flexible workflow, powered by various commands, offers developers the freedom to customize their working environment to suit their specific needs and preferences.
Each change made to the codebase is recorded through commits, accompanied by meaningful messages that provide context and clarity about the modifications.
Git also excels in its search functionality, enabling developers to efficiently navigate through the project's history and revert to previous versions if needed.
Additionally, Git supports hosting on various platforms like GitHub, GitLab, and Bitbucket, making it accessible and adaptable to different hosting environments.
Git revolutionises version control in software development, empowering teams to collaborate effectively, manage code changes seamlessly, and maintain a high level of productivity throughout the development lifecycle.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁 -𝗮 -𝗺 "𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁 𝗺𝗲𝘀𝘀𝗮𝗴𝗲": Commit all tracked changes with a message.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘁𝘂𝘀: Show the state of your working directory.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗮𝗱𝗱 𝗳𝗶𝗹𝗲_𝗽𝗮𝘁𝗵:Add file(s) to the staging area.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗰𝗸𝗼𝘂𝘁 -𝗯 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Create and switch to a new branch.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁 --𝗮𝗺𝗲𝗻𝗱:Modify the last commit.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗽𝘂𝘀𝗵 𝗼𝗿𝗶𝗴𝗶𝗻 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Push a branch to a remote.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗽𝘂𝗹𝗹: Fetch and merge remote changes.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝗯𝗮𝘀𝗲 -𝗶: Rebase interactively, rewrite commit history.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗹𝗼𝗻𝗲: Create a local copy of a remote repo.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗺𝗲𝗿𝗴𝗲: Merge branches together.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗹𝗼𝗴 --𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘁: Show commit logs with stats.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝘁𝗮𝘀𝗵: Stash changes for later.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝘀𝗵𝗼𝘄 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁_𝗶𝗱: Show details about a commit.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝘁 𝗛𝗘𝗔𝗗~𝟭 or git reset "commit #code" (obtained from log): Undo the last commit, preserving changes locally.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗮𝗽𝗽𝗹𝘆 𝗽𝗮𝘁𝗰𝗵_𝗳𝗶𝗹𝗲_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Apply changes from a patch file.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵 -𝗗 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵_𝗻𝗮𝗺𝗲: Delete a branch forcefully.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝘁: Undo commits by moving branch reference.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘃𝗲𝗿𝘁: Undo commits by creating a new commit.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗰𝗵𝗲𝗿𝗿𝘆-𝗽𝗶𝗰𝗸 𝗰𝗼𝗺𝗺𝗶𝘁_𝗶𝗱: Apply changes from a specific commit.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗯𝗿𝗮𝗻𝗰𝗵: Lists branches.
𝗴𝗶𝘁 𝗿𝗲𝘀𝗲𝘁 --𝗵𝗮𝗿𝗱: Resets everything to a previous commit, erasing all uncommitted changes.
git checkout branch-name

Comments
Post a Comment